Soil resistivity testing is a method of determining the electrical impedance of soil, by measuring how soil depth impacts the design of electrical earthing systems. The soil’s resistivity rating determines how well it conducts electricity, which is essential for earthing system design to provide the appropriate level of safety and protection for an electrical power system.
Why Is Soil Resistivity Testing Important?
Having a strong soil structure is a foundational requirement for the electrical earthing design process. By undertaking soil resistivity testing before implementing an electrical earthing design, project managers and engineers can identify where potential flaws could occur depending on soil strength, and incorporate the appropriate solutions into the design.
An earthing system is designed to dissipate any fault current that may flow through it, and the soil resistivity influences the earthing system’s ability to do so. Therefore, a low soil resistivity means that the earthing system will have a lower impedance and be able to dissipate more fault current. On the other hand, a high soil resistivity implies that the earthing system will have a higher impedance and be less effective at dissipating fault current. This can potentially result in a higher-than-expected voltage in the earthing design and lead to operational failures or over current in devices attached to the network.
Because of this, it is critical to accurately determine the soil resistivity before designing an earthing system.
How Does Soil Resistivity Testing Work?
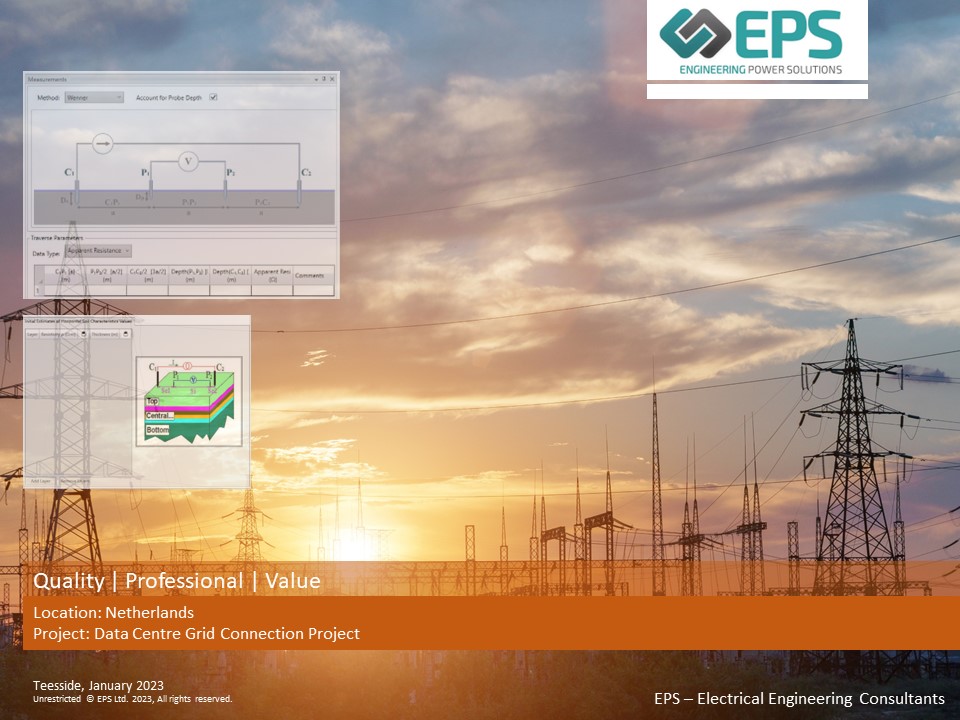
There are several methods of testing soil resistivity, including the reliable Wenner array method, the most appropriate method should be selected based on your site conditions.
In all cases, soil resistivity testing is conducted by measuring the voltage across a known length of conductor in the soil. The soil’s resistivity is then calculated based on the measured voltage and the known conductor length. Soil resistivity testing can determine the suitability of soil for new earthing system design, as well as to optimise the design of existing earthing systems to meet the specific needs of a project.
The Wenner 4-Point Array Test
The Wenner 4-Point Test is one of the most common methods used for testing soil resistivity. The test is conducted by placing four electrodes in the ground at equal intervals and passing an electrical current between two of the electrodes. The spacing between the electrodes can be varied, but is typically between 50 cm and 1 m. The resulting voltage is then measured between the other two electrodes. This process is repeated with the electrodes in different positions, and the results are used to calculate the soil resistivity. The Wenner 4-Point Test is a relatively simple and inexpensive way to test for soil resistivity, and it is frequently used in determining electrical earthing design parameters for a variety of projects.
Next Steps
At Engineering Power Solutions, we provide tailored earthing design services from 400kV, 275kV 132kV, 33kV 11kV and 415V systems to identify areas of electrical risk and improve health and safety, including soil resistivity testing. For more information or to discuss your project requirements, please contact one of our engineers today.










